TINY OFF-GRID HOUSE LOW-E GLASS WINDOWS
Image courtesy of Ecopro Windows & Glass
When installed properly, Energy Star windows can be a functional component of a tight building envelope that will help maintain energy efficiency and the insulated envelope of the Tiny Off-Grid House.
ENERGY STAR® WINDOWS
According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) “air leakage accounts for between 25 percent and 40 percent of the energy used for heating and cooling in a typical residence.” The EPA recommends the use of ENERGY STAR certified windows to “lower energy bills, keep your homes inside temperature consistently comfortable and reduce UV sunrays damage to floors, carpets, and furniture.” ENERGY STAR certified windows, doors and skylights “are independently tested and verified by the National Fenestration Rating Council (NFRC) “that meet strict energy efficiency guidelines set by the EPA.”
WINDOW INSULATION
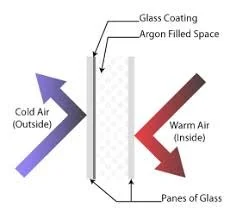
A traditional single pane of glass is a poor insulator easily allowing the transfer of heat through the glass. The rate of heat transfer though a material is measured by the U-factor. The U-factor ranges between 0.20 and 1.20, with a lower number representing better performance. ENERGY STAR windows have two or more panes of glass to increase resistance reducing heat transfer by serving as a thermal break.
The Tiny Off-Grid House will require windows with a minimum of two panes of glass; more than two panes of glass may have diminishing returns compared to similar investments made in high R-value insulation in the walls, roof and trailer.
Image courtesy of Economy Glass
Another technology used to reduce the conductive loss of heat is to fill the spaces between the panes of glass with an insulating transparent gas; such as Argon (Ar) gas. Argon gas is the third most abundant gas in the earths atmosphere and more dense than air. Argon is a dry, colorless, odorless, nonreactive and nontoxic metallic coating on the inner surface of the exterior pane of an insulated double panes window. Argon gas reduces radiant heat transfer between the glass panes. The Argon gas insulation also dampens the transmission of sound. Another insulation gas is Krypton which is a more efficient insulator of Low-E windows. If the insulated space(s) in multi panes windows exhibit signs of fog or condensation this may indicate the insulation seal has been compromised.
Heat usually travels toward cold. As the inside warm humid air comes in contact with a cold surface, it condenses in to water droplets often seen accumulating on a cold glass surface (Warm airborne H2O + Cold surface = Condensation). Multi pane windows prevent condensation by separating the warm interior window pane from the colder outside window pane. The effectiveness is measured by the Condensation Resistance (CR) ranged 1 - 100. A higher number dual pane window represents a greater resistance to the formation of condensation on the glass surface.
Although multi-pane windows are not specifically intended to be soundproof (Soundproof = 45 - 50 on the Sound Transmission Class Scale) dual pane windows rate around 26 STC which can dampen some noises. This added benefit can add to the quality of life in the Tiny Off-Grid House.
LOW-E WINDOWS
Low-Emissivity (Low-E) coating enable energy-efficient windows to block the Suns’ radiant energy and ultraviolet (UV) . Low-E windows have a clear thin non-toxic silver or tin oxide coating on the inner side of the exterior glass to block the heat waves from sunlight (Infrared light) from entering the house. The Low-E coating is 150 nanometers thick; for comparison, the thickness of human hair is 75,000 nanometers.
Emissivity is the quantifiable measure of heat waves ability to pass through a material. Regular glass has an emissivity rating of 0.84; or in other words, 84% of heat waves can pass through regular glass; Low-E windows have an emissivity of 0.02 (20%).
Image courtesy of Accessibility Tools
Low-E windows can block most UV light, which can cause fading to floors, fabrics and furniture. Low-E windows combined with dual pane windows can block 84% of UV rays and up to 86% with triple pane windows. Low-E should not be confused with tinted windows, both block UV and infrared light; however, only tinted windows block sunlight.
SUSTAINABLE WINDOWS
An ENERGY STAR certification is primarily focused on the energy savings performance of the window and does not judge the sustainability of the manufacturing process or the end product. The material and manufacturing process of the window can impact indoor air quality. The Tiny Off-Grid House emphasizes both performance and sustainability in building construction.
Fiberglass window frames are more energy efficient and durable than vinyl. Fiberglass has less thermal conduction than aluminum and weigh less. Also, fiberglass frames require less maintenance (Painting, sealing) compared to wood frames. Unlike wooden frames, fiberglass frames are less prone to warping, moisture damage, swelling and rot over time. Vinyl frames cannot be painted but fiberglass can be painted and textured to even mimic the appearance of wood if desired.
Most fiberglass composites are made from recycled glass; which is made from an abundant resource, sand; infused with polyester resins. Vinyl is made from Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) which is very difficult to recycle. The manufacturing process of fiberglass is non-toxic to the environment and the finished product does not lower indoor air quality by off-gassing. The manufacturing process of vinyl produces harmful chemicals. Vinyl also has the potential to release harmful fumes in the house when burned by fire.
WINDOW DESIGN
The starboard, square picture window is stationary and does not open; unlike the remaining awning (aka Top hinged windows) windows of the Tiny House that opens outward at their base. This feature of an awning window helps keep rainwater out even when the window is fully open. The large square picture window will be made of tempered safety glass. If it should break, blunt cubes, as opposed to sharp jagged pieces, are formed.
The Tiny Off-Grid House picture window dining area will allow for spectacuar views outside for persons eating or working at the long horizontal bar table with two stools. The bar table is positioned at a height to perform task while seated on a stool or while standing. The picture window allows sunlight to flow inside filling the living space with illumination. A potential benefit is the natural radiant sunlight heating the floor mass in the living space during daylight hours which will act as a thermal energy reserve slowly releasing the stored heat at night.
The large picture window has the potential to facilitate passive solar house heating, reducing electrical energy needed for lighting and heating, while also providing a decorative open feeling to the Tiny Off-Grid House and a full view of nature. The picture window will be orientated in the same direction of the rooftop solar array, facing south, to receive maximum sunlight in to the house.
The strength of the fiberglass affords for a thinner frame allowing more visible glass which increases the sunlight and view of the scenery.
No windows will be installed on the bow side due to the potential for road debris to break the glass during transport.
The ground level bathroom awning window is designed with an “obscure” style glass pattern that provides privacy while allowing sunlight in.
Each awning window, fully extends outwards, allowing emergency egress directly to the outside. The International Building Code requires atleast one window suitable for emergency egress in every sleeping loft. An emergency egress window should measure, no less than, 24” H (610 mm) x 20” W (508 mm) with an unblocked open area no less than 5.7 Sq. Ft. (0.530 m2). (2018 International Building Code, Appendix Q, R310.2.1 Minimum Opening Area)
There are two types of Low-E glass: Solar Control Low-E and Passive Low-E:
Solar control Low-E coating is manufactured using the Magnetron Sputtering Vapor Deposition (MSVD) process. Solar control glass has low emissivity and is best used in hot and humid environments. The lower emissivity of the glass blocks most penetration of the suns’ thermal short-wave energy from entering and heating the house.
Passive Low-E coating is manufactured using the Pyrolytic process and is best used for cold environments requiring passive solar heating. The high emissivity allows the sun’s short-wave infrared energy to penetrate the glass heating the house. The Suns’ visible light is allowed to shine through the glass panes to illuminate the inside reducing the need for electrical lights during the day. The Suns’ short wave radiant energy passively heats the floor mass and surfaces during the days to be slowly released at night; in the form of passive solar heating. Inaddition, the interior long-wave heat energy is reflected back inside.
The solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC) is the windows ability to block the transfer of radiant heat through the glass. The SHGC ranges between 0 and 1, with a lower number representing better performance. A high SHGC means more solar heat radiation is shining in to the living space, which can be beneficial in colder climates for passive heating. Conversely, a low SHGC is beneficial in warmer climates to reduce the amount of air conditioning needed for cooling.
In the harmony of sustainable renewable energy, the ideal would be to use passive solar heating to supplement the primary indoor heating system (Mini split). However, initial research reveals this may cause excessive heat gains in the summer which will cause greater energy usage to keep the Tiny House cooler. Therefore, the priority of the Tiny Off-Grid House will be energy efficiency by maintaining an insulated envelope with Low-E windows, with a solar control Low-E coating, that blocks the penetration of unregulated solar radiant energy through the glass which can overheat the house in the hotter season. Extreme heat events, caused by climate change, are increasing in intensity & frequency.
Please share your thoughts or experiences in the Comments section below.